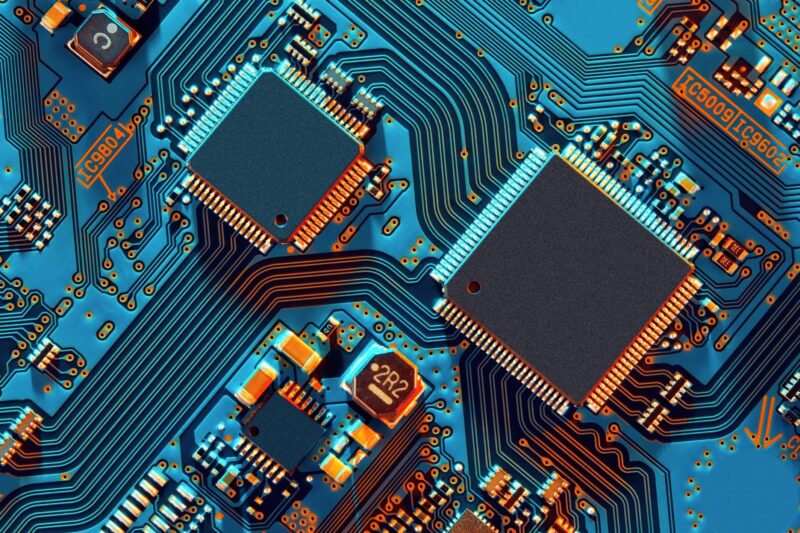
Miniaturization of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) designs is a rapidly growing field that presents both challenges and opportunities for innovators. Recent advancements in materials, components, and manufacturing processes have opened the door to an entirely new set of possibilities for PCB design engineers.
From ultra-small form factors to complex multi-layered boards with multiple types of circuitry, miniature PCBs are making it easier than ever to create products that were previously impossible or impractical due to size constraints. Despite these advances, designing miniaturized printed circuit boards still requires careful consideration of several key issues such as space utilization, signal integrity, power delivery, thermal management and cost optimization.
This article will discuss the various challenges associated with miniaturizing printed circuit board designs as well as the innovative approaches being adopted by leading companies to overcome them.
Power and Heat Dissipation Considerations
As PCB designs become increasingly miniaturized, power and heat dissipation considerations must be taken into account. Heat can create a number of issues, such as destabilizing electronic components or causing them to overheat.
To prevent this, designers often use methods such as increasing airflow or adding thermal vias between layers of the board. Power delivery networks are also an important factor when it comes to miniaturization – they must be able to efficiently transfer energy from one component to another in order to avoid overloading any particular part of the circuit.
In addition, it is critical for designers to ensure that their boards remain within safe temperature and voltage constraints in order for them to function properly without any risk of failure. Finally, other factors such as signal integrity should also be taken into account when designing miniature PCBs – these may include impedance matching techniques and using shielding materials which reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). All these considerations are essential for creating reliable and functional miniaturized PCBs which can operate safely under various conditions.
Cost Limitations Innovations

Cost limitations can be a challenge in miniaturizing printed circuit board (PCB) designs, but technological advances have enabled innovations that make it possible to reduce costs and design PCBs in smaller sizes. One such innovation is the use of high-density interconnect technology, which allows more connections per unit area than standard methods.
In addition, surface mount technology has been developed to enable components to be placed on both sides of the board without increasing their size. This helps keep cost down while still allowing for a reduction in PCB size.
Furthermore, multi-layer boards with built-in circuits are becoming increasingly common as they further reduce the space needed by combining multiple layers into one compact component. Finally, 3D printing techniques allow for complex shapes to be created within restricted spaces – something conventional manufacturing methods cannot achieve – making them an ideal solution when designing small PCBs where space is at a premium.
High Density Interconnects (HDI)

High Density Interconnects (HDI) have become an increasingly popular choice for miniaturized PCB designs. HDIs are boards that feature a high number of components in a small area, with up to 24 layers or more. This type of design enhances signal integrity and reduces power consumption while delivering higher performance than traditional printed circuit boards.
With the ability to reduce overall board size, HDIs offer great advantages when it comes to miniaturizing products such as medical equipment and consumer electronics. The challenges presented by high density interconnects include their complexity; with so many components packed into such limited space, there is the potential for overcrowding and increased risk of failure due to signal interference or cross-talk.
Additionally, HDI fabrication requires intricate drilling which can be time consuming and costly if done incorrectly. Another issue is that traces may need to be rerouted if any modifications are made during assembly, resulting in additional time and cost expenditure again.
Conclusion
Miniaturization of PCB designs is an ever-evolving process, with challenges and innovations being explored every day. With advancements in technology, engineers have been able to create smaller components that allow for higher density boards and provide much more reliable performance.
However, designing a small board requires careful consideration of the design constraints as well as knowledge on how to optimize the circuit layout. By researching new techniques and staying up-to-date with industry trends, designers can ensure their products are competitively manufactured and meet customer needs.
To learn more about miniaturization challenges and innovations in PCB design, contact your local engineering team for further assistance.